Projects
Synaptotagging
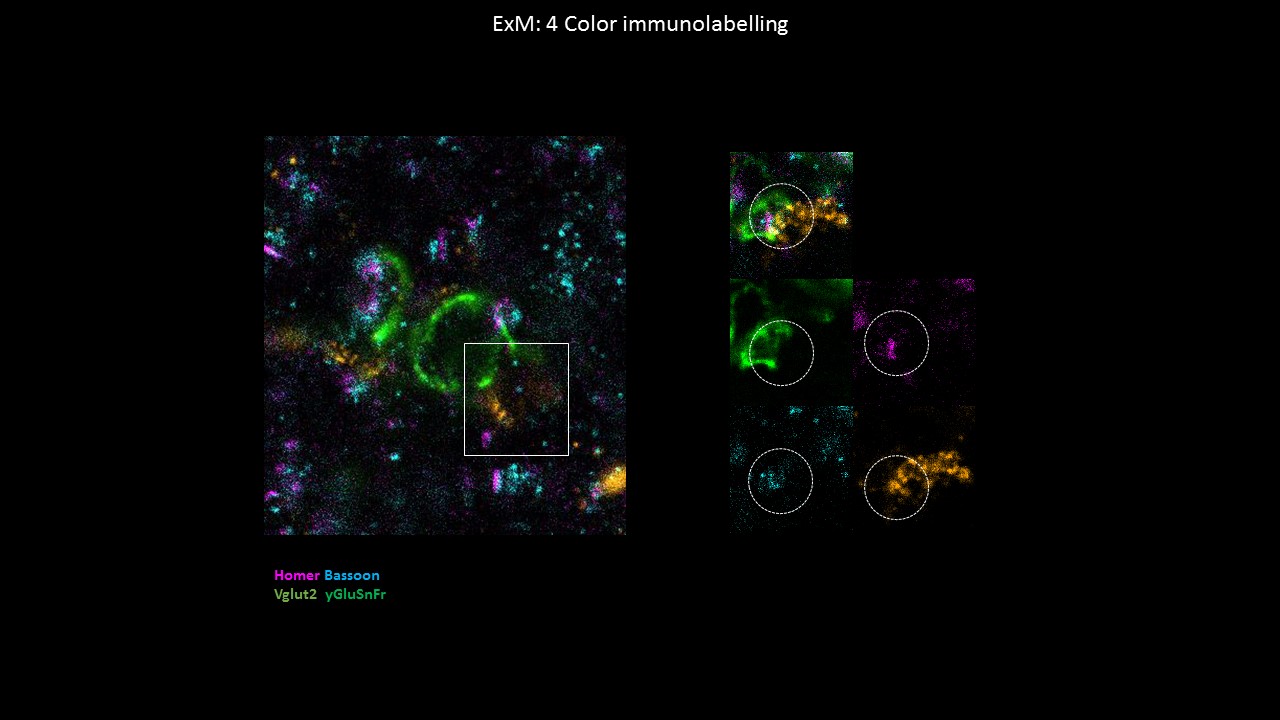
Elucidating computations performed by a given neuron depends on measuring its synaptic inputs from multiple brain regions, yet identifying projection-specific synapses in vivo remains a difficult task. Here we describe a method to identify thalamic inputs onto labeled cortical neurons in vivo as an application of dendritic glutamate imaging. Our method employs structured two-photon imaging of sparsely expressed iGluSnFR glutamate sensor at dendrites and optogenetic stimulation of presynaptic cell bodies. This technique mapped long-range glutamatergic inputs from the ventromedial thalamic nucleus (VM) to the apical tufts of pyramidal tract (PT) neurons in layer 5B of anterolateral motor cortex (ALM) in mice. By systematically varying the pulse timing of optogenetic stimuli with respect to the imaging frame and averaging over trials, we detected glutamate transients at millisecond effective resolution with conventional two-photon raster scans. Measurements of synaptic latencies with iGluSnFR discriminated monosynaptic and polysynaptic inputs. A subset of mapped inputs were validated post-hoc with four-color expansion microscopy that labeled the presynaptic and postsynaptic structures, including iGluSnFr reporter, vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (VGluT2), Homer1, and Bassoon. Our work demonstrated that postsynaptic glutamate measurements with optogenetic stimulation detect projection-specific, monosynaptic inputs at cortical dendrites.
Dendritic glutamate imaging
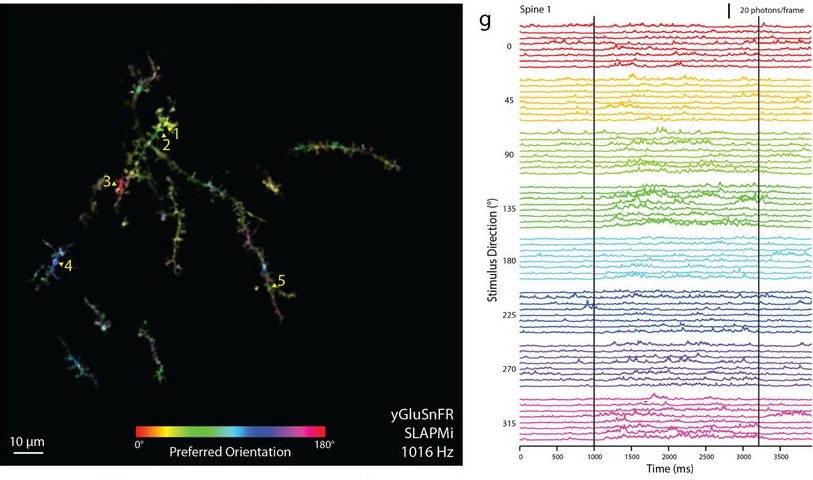
Combining high-speed two-photon imaging and glutamate sensors provides a way to monitor synaptic inputs to any given neuron. Mapping anatomically defined synapses and measuring receptive fields of said synapses during behavior is a powerful method to characterizing how a neuron transforms its input parameters.
In vivo voltage imaging
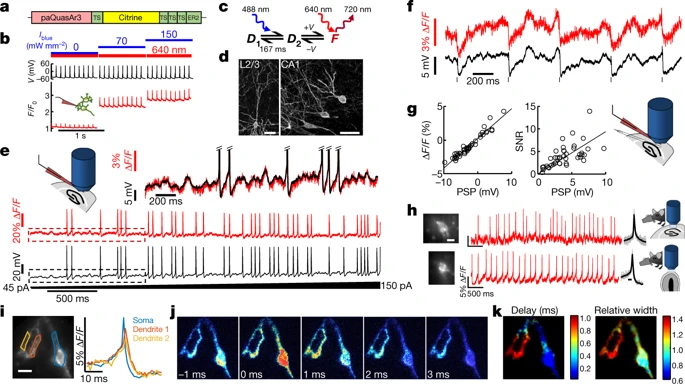
The strength of voltage imaging lies in its ability to monitor the membrane potential, including subthreshold activity, in dozens of neurons simultaneously. This type of measurement cannot be accomplished by other methods, save for laborious multi-patching. Measuring subthreshold activity during behavior offers subtle clues as to how the network wires and fires.
